A Simple Guide to DPoS: Blockchain Voting System That Could Transform Democracy
Electronic voting offers faster results, reduced costs, and the potential to increase voter participation. Yet concerns about security, transparency, and manipulation have slowed its broader adoption. Blockchain technology introduces a promising foundation for secure and verifiable digital voting. Among various blockchain consensus methods, Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) stands out as particularly well-suited for building trusted voting systems.
- What Is DPoS? A Simple Explanation
- Why DPoS Is a Good Fit for Voting Systems
- How Voting and Delegation Work in DPoS
- How DPoS Differs from Other Blockchain Methods
- Key Features That Support Safe, Transparent Voting
- Challenges to Consider
- Real-World Applications of DPoS Voting
- Why DPoS Could Shape the Future of Voting
- Final Thoughts
If you’re new to blockchain or the concept of DPoS, this guide explains it in straightforward terms, no technical background required.
What Is DPoS? A Simple Explanation
Consider an example of organizing a fair election. Instead of allowing everyone to directly manage the process, people vote for a trusted group to handle it on their behalf. That’s the basic idea behind DPoS.
In traditional blockchain systems like Bitcoin, computers (or nodes) compete to confirm transactions, a process that consumes a lot of time and energy. DPoS takes a different path. Rather than relying on computational power, it lets users vote to elect a small number of trusted participants called delegates to verify transactions and maintain the system.
If these delegates act responsibly, they remain in place. If they fail to perform or act unfairly, voters can quickly replace them. Think of it as electing officials who don’t make laws but ensure the blockchain works properly and securely.
Why DPoS Is a Good Fit for Voting Systems
In any election, trust is key. Voters want assurance that their vote counts, their privacy is respected, and the final tally is accurate. DPoS supports all of these goals by decentralizing control and ensuring that the system is governed by the people who use it.
Since delegates are elected and can be voted out at any time, the system remains transparent and accountable. And because it runs on blockchain, every vote is recorded permanently and cannot be changed, creating a public audit trail without compromising individual voter privacy.
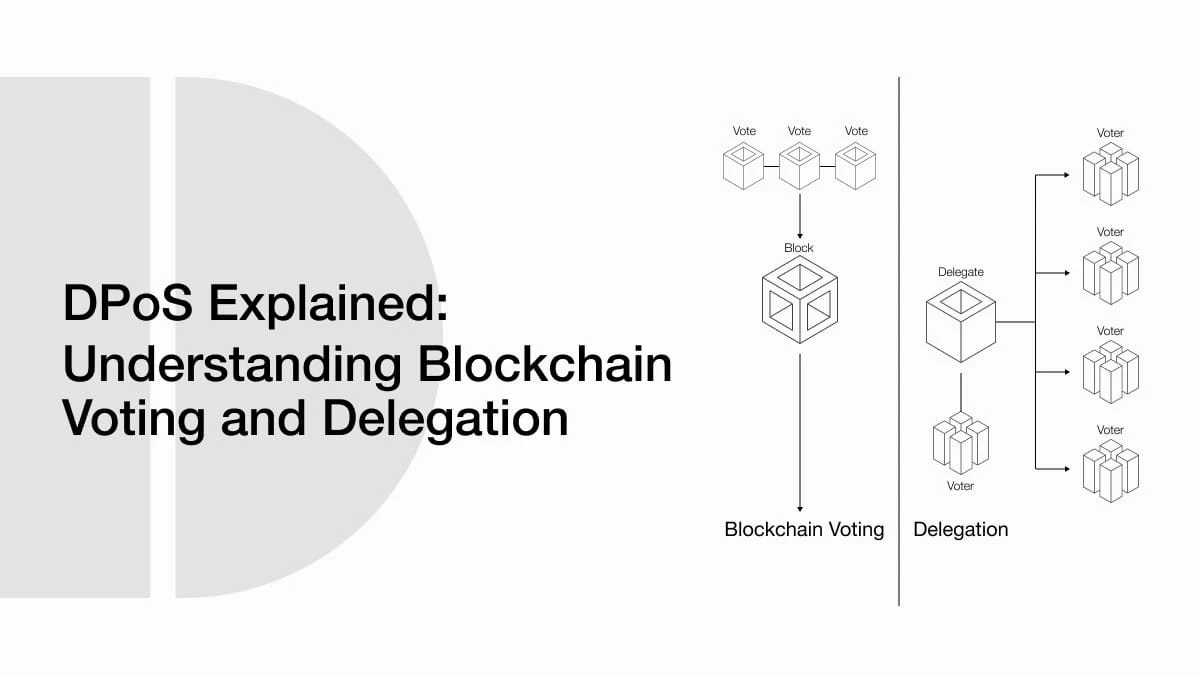
How Voting and Delegation Work in DPoS
Here’s how a DPoS-based voting system works:
- Identity verification: Each participant must prove their identity before voting.
- Vote casting: Voters submit their choices, which are securely encrypted and added to the blockchain.
- Delegate election: Voters also use their influence to elect delegates who supervise the system, validate votes, and maintain transparency.
Everyone who holds tokens in the network has voting power, which helps prevent any single entity from taking control.
How DPoS Differs from Other Blockchain Methods
You may have heard of other blockchain models like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS):
- PoW (used by Bitcoin) requires solving complex puzzles to validate transactions, consuming vast energy and time.
- PoS selects validators based on how many tokens they hold and are willing to “stake.”
Delegated Proof of Stake introduces a more democratic and efficient approach. Instead of random selection or resource competition, it uses a community voting system to choose who maintains the blockchain. As a result, it operates faster, uses less energy, and offers a more flexible governance model.
Also Read: What Is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)? A Beginner’s Guide
Key Features That Support Safe, Transparent Voting
DPoS-based voting systems are designed to meet the essential requirements of modern elections:
- Privacy: Advanced encryption ensures that votes remain confidential and cannot be traced back to individuals.
- Auditability: Voters can verify that their vote was counted, and independent observers can confirm the accuracy of the final results.
- Security: Every vote is stored immutably on the blockchain, making tampering virtually impossible.
- Efficiency: With a small number of trusted delegates managing the process, DPoS systems can handle results more quickly than older consensus models.
Challenges to Consider
While DPoS offers many advantages, it is not without challenges:
- Scalability: Handling millions of votes in real time still requires significant infrastructure and optimization.
- Voter authentication: Ensuring that only eligible voters can participate (and only once) is critical and requires integration with secure identity systems.
- Public understanding: For Delegated Proof of Stake to gain trust in public elections, people must understand how it works. If the system seems too complex, it may face resistance, making clear communication and education essential.
Real-World Applications of DPoS Voting
DPoS-based voting systems have already been tested in various settings, from student government elections to board decisions and small-scale municipal votes. Platforms like Voatz, Polys, and Follow My Vote are experimenting with blockchain and DPoS to enhance democratic processes.
While these systems are not yet ready for nationwide elections, they demonstrate that DPoS is more than a theory; it’s already being put into practice.
Why DPoS Could Shape the Future of Voting
Delegated Proof of Stake blends community decision-making, high-speed performance, and strong security, all of which are essential for trustworthy electronic voting. It reduces reliance on central authorities, empowers voters to hold validators accountable, and ensures that every vote is recorded permanently and accurately.
For governments, institutions, and organizations exploring secure digital elections, DPoS offers a promising path forward. With ongoing development and public engagement, it could play a major role in the evolution of modern voting systems.
Final Thoughts
Though the term “Delegated Proof of Stake” may sound technical, the concept is surprisingly straightforward: it empowers people to vote for trusted representatives who maintain a fair and secure voting process on the blockchain.
As interest in reliable digital voting continues to grow, DPoS has the potential to support transparent, efficient, and tamper-proof elections on a larger scale. Whether you’re a policymaker, a developer, or simply a curious voter, understanding how Delegated Proof of Stake works is a valuable first step toward shaping the future of democracy.