How Decentralized Social Media Could Use DPoS for Content Moderation
Social media has become a way of life. People use it to post their ideas, news, or just about anything that happened in their day. Apps such as Facebook, Instagram, and X (formerly Twitter) are the most popular places where billions of people go to stay connected. However, as much as these platforms are extremely powerful, they also have some major problems. One of the largest? Content moderation.
- What is Decentralized Social Media?
- A Simple Explanation
- Problems with Centralized Social Media
- Why Decentralization is Needed
- What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)?
- The Basics of DPoS
- How Delegates Work
- Why DPoS Fits Social Media
- PoW vs PoS vs DPoS
- Why Content Moderation Matters in Social Media
- The Challenge of Moderation
- The Current Centralized Approach
- Why a New System is Needed
- How DPoS Could Power Content Moderation in Decentralized Social Media
- Voting for Content Moderators
- Community Flagging and Review
- Smart Contracts for Fair Rules
- Example of How it Works
- Steps in DPoS Content Moderation
- Incentives and Rewards in DPoS Moderation
- Why Rewards Matter
- Token-Based Incentives
- Punishment for Abuse
- Example: Reward Flow in Action
- Case Studies and Research Insights
- Lessons from Existing Decentralized Platforms
- Academic Research on Blockchain Social Media
- Takeaway
- Benefits of Using DPoS for Moderation
- More Transparency
- Faster and Scalable
- Stronger Community Engagement
- Example of the Benefits in Action
- Challenges of DPoS in Moderation
- Risk of Token Cartels
- Risk of Biased Delegates
- Technical Barriers
- Example of Challenges in Action
- Future of Content Moderation with DPoS
- Integration with AI
- Building Reputation Systems
- Global Adoption
- Example of the Future in Action
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions About How Decentralized Social Media Could Use DPoS
- What is DPoS in simple terms?
- How can DPoS help in content moderation?
- Is decentralized social media safe?
- What are the risks of DPoS in moderation?
- Which social media platforms are decentralized?
- Glossary of Key Terms
Content moderation is basically about blocking harmful posts, stopping fake news from spreading, and trying to keep the space safe for everyone. The problem is that big tech companies mostly do it. They’re the ones deciding what gets to stay online and what gets removed. And honestly, a lot of people don’t really like that. Some say it gives too much power to one company. Others complain that bad content sits around for way too long, while harmless posts get taken down for no clear reason.
That is why people are now turning to decentralized social media. A decentralized network, unlike normal platforms, provides users with greater control over their data and decisions. Rather than one company running the show, power is shared across many users and computers. This renders the platform less secretive and open to censorship. Still, even decentralized platforms need a way to deal with moderation. Otherwise, fake news, hate speech, and spam could just take over. The real question is: how do you build a system that keeps people safe without silencing voices?
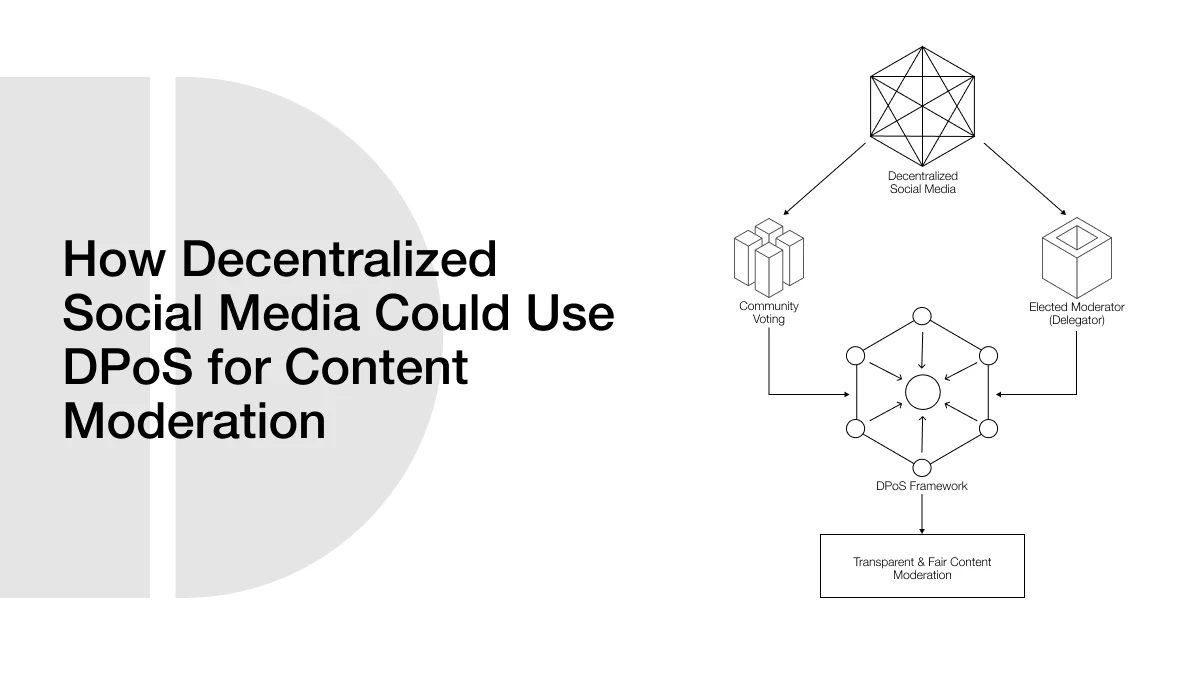
One possible answer is something called Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). It’s a blockchain method where users vote for trusted people, called delegates, to make decisions for the group. Typically, it’s used for approving crypto transactions. But the same idea could be used for moderation, too. Users could vote for moderators, and those moderators would decide which content to keep and which to remove.
ALSO READ: Breaking Barriers: Why DPoS Could Be the Future of Borderless Credit and Microfinance
What is Decentralized Social Media?
A Simple Explanation
Decentralized social media is a new twist in the way people use online platforms. Instead of one big company being in charge of everything, the system spreads control across a network of computers. This happens with the help of blockchain and peer-to-peer technology, which makes it harder for any single group to take over.
On normal platforms like Facebook or Instagram, the company is in charge. They decide how your data is used, they make the rules, and they determine which posts are posted or removed. With a decentralized platform, stuff doesn’t work that way. The control is now in the hands of the users themselves. The rules are typically encoded into smart contracts on the blockchain, so they can’t be altered secretly afterwards.
Problems with Centralized Social Media
Centralized platforms may be popular, but they bring numerous issues. The biggest one is too much power in one place. When a single company decides what is allowed and what is not, people often feel like they’re being silenced or treated unfairly.
Privacy is another big concern. Many of these platforms collect user data and sell it to advertisers without people even realizing how much is taken. Moderation also feels uneven. Sometimes a post gets deleted while another, equally harmful one, is left online. This inconsistency makes people lose trust.
And then there’s censorship. Centralized platforms can be pressured by governments or big corporations to take down certain voices. For users, this feels political or motivated by money, which creates even more mistrust in the system.
Why Decentralization is Needed
Decentralized social media provides an escape from these issues. Since no one company owns the network, there is increased freedom for the user. Transparency is established since they can track decisions on the blockchain. Decentralized systems are also more privacy-related, as data is not concentrated in a single location and sold to advertisers.
The most interesting thing about decentralization is that authority is returned to the community. As opposed to the choice being made by one company as to what is to be kept, the community is given the option. This is where systems like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) come into play. With DPoS, the users vote on who they trust, and these trusted parties do the moderation tasks in a way that is supposedly fair and transparent.
There is already a glimpse of this idea in sites such as Mastodon, Diaspora, and Steemit. All of them demonstrate that individuals are willing to take control of their online areas. And studies indicate that by combining blockchain with technologies such as IPFS (InterPlanetary File System), it is possible to create social networks that are much more difficult to censor and much less centralized to control by one authority figure (Adarsh & Kaur, 2024).
What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)?
The Basics of DPoS
Delegated Proof of Stake, DPoS, is a method of blockchains reaching consensus on what is true. It is a voting mechanism that assists in determining who is to confirm transactions and keep the network going.
In Proof of Work (PoW), as in Bitcoin, computers compete to solve puzzles, an energy-intensive process. The concept of Proof of Stake (PoS) is that participants stake coins to verify transactions. Rather than each person trying to validate, the users vote for a smaller number of people referred to as delegates. These representatives then decide on behalf of the network.
This makes DPoS faster and more efficient than other systems. It also feels more democratic because users get to choose who represents them.
How Delegates Work
In DPoS, users vote with their tokens. The people or groups who receive the most votes become delegates. Delegates are responsible for checking transactions, adding new blocks, and maintaining system fairness.
If a delegate does not perform well, the community can vote them out and choose someone else. This creates accountability. Delegates know that if they act unfairly, they can quickly lose their position.
Why DPoS Fits Social Media
The idea of voting for trusted delegates can also be used in social media moderation. Imagine a system where, instead of a company deciding what post to remove, users vote for moderators they trust. These moderators, like blockchain delegates, can review flagged content and decide if it should stay or be removed.
This way, content moderation becomes faster, community-driven, and transparent. The rules for how decisions are made can even be written into smart contracts, which makes the process clear for everyone.
PoW vs PoS vs DPoS
| Feature | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) | Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) |
| Speed | Slow | Medium | Fast |
| Energy Use | Very High | Lower | Very Low |
| Governance | Miners control | Stakers control | Delegates elected by users |
| Best Use | Bitcoin | Ethereum 2.0 | Social media, fast transactions |
This table shows why DPoS stands out. It is faster, uses less energy, and has a built-in voting system that matches well with the needs of decentralized social media moderation.
Why Content Moderation Matters in Social Media
The Challenge of Moderation
Social media has provided a platform to everyone to speak, but the fact is that not all voices are safe or even beneficial. Malicious content such as fake news, hate speech, and unending spam spreads quicker than you imagine. Without anyone to moderate, a platform may become a very unhealthy place, where people may not feel safe. Conversely, in case moderation is taken to extremes, users can end up feeling that they are being censored.
It is the balancing act that is tricky. Platforms must ensure the safety of people against harmful content, yet they must also respect free speech. Finding that balance is one of the most difficult tasks a social media company faces.
The Current Centralized Approach
Right now, most major platforms rely on a centralized moderation system. Companies like Meta (which runs Facebook and Instagram) or X (Twitter) hire large teams of moderators and also depend on artificial intelligence to filter content. It works to an extent, but it comes with major problems:
- Bias and inconsistency: It is commonly observed that some of the harmful posts remain up, whereas others are deleted unfairly.
- Opaque rules: The rules are difficult to understand, and the decisions are not always clearly articulated.
- Slow response: Harmful content can remain for hours or even days before it’s removed.
- Mistrust: Most users believe that decisions are made on the basis of politics, profit, or external pressure.
Due to such problems, the trust in centralized moderation has been reduced. Most of the users believe that the system is not really fair, and this destroys their trust in the platforms themselves.
Why a New System is Needed
A new approach is needed where moderation is transparent, community-driven, and fair. Instead of one company making all the decisions, users themselves can have a say.
In decentralized social media, content moderation can be done with blockchain-based systems like DPoS. Here, the rules are clear, and everyone can see how decisions are made. Users can vote for trusted delegates to handle moderation, and those delegates are accountable to the community.
This solves many of the problems of centralized moderation:
- Decisions are open and visible.
- Power is shared instead of concentrated.
- Communities can adapt rules to their needs.
As researchers note, decentralized systems using blockchain and IPFS aim to reduce reliance on centralized platforms and give users more power over moderation and data ownership (Adarsh & Kaur, 2024).
| Feature | Centralized Moderation | DPoS-Based Moderation (Decentralized) |
| Who Decides? | Company employees + AI | Delegates elected by users |
| Transparency | Low, hidden decisions | High, rules written in smart contracts |
| Speed | Medium (AI helps, but delays) | Fast (small group of elected delegates) |
| Trust from Users | Low, often mistrusted | Higher, since the community is involved |
| Adaptability | Hard to change | Easy to adapt by community vote |
This comparison shows why decentralized social media needs a new system. DPoS provides the right mix of speed, fairness, and accountability.
How DPoS Could Power Content Moderation in Decentralized Social Media
Voting for Content Moderators
In a DPoS system, users do not moderate everything themselves. Instead, they vote for trusted delegates who act as content moderators. Just like in a democracy, the people choose representatives.
If you are a user on a decentralized social media platform, you can use your tokens to vote for someone you trust. These moderators are people who are elected to decide on content. The moderators receive several votes based on community support. When a moderator ceases to be fair, the users can vote him out and elect somebody else.
ALSO READ: DPoS Governance Insurance: Can Delegators Hedge Against Delegate Failure?
This makes a system whereby the moderators understand that they have to do the right thing. They will lose their role in case they abuse their power.
Community Flagging and Review
The moderation process begins with the community. Users can flag harmful posts such as hate speech, spam, or fake news. Once flagged, the post is sent to the group of elected delegates.
These delegates then review the flagged content. They decide, by voting among themselves, whether the post should be removed, limited in visibility, or allowed to stay. This decision is fast because only a small group of delegates is involved, not the entire user base.
Smart Contracts for Fair Rules
The moderation rules are written into smart contracts on the blockchain. A smart contract is a piece of code that runs automatically and cannot be secretly changed. For example, the rules might say:
- If more than 60% of delegates vote to remove content, it is taken down.
- If a flagged post is proven false, the reporter gets rewarded.
This way, everyone knows the rules, and no hidden policies exist. The process is transparent and open for anyone to see.
Example of How it Works
Let’s imagine someone posts fake news on a decentralized platform. A user sees it and flags it. The post is now sent to 20 elected delegates. Out of those, 15 vote that it is harmful. Because the smart contract rule says more than 60% agreement is needed, the post is removed. The user who flagged it first may even earn a small reward for helping keep the platform safe.
This process is fast, fair, and community-driven.
Steps in DPoS Content Moderation
| Step | Who Acts? | What Happens? |
| 1. User flags content | Regular users | A suspicious post is reported. |
| 2. Delegates review | Elected moderators | Delegates check if the flag is valid. |
| 3. Voting takes place | Delegates | Decision is made (keep, remove, or restrict). |
| 4. Smart contract applies | Blockchain system | The rule is enforced automatically. |
| 5. Incentives rewarded | Reporter or honest delegate | Tokens or reputation points are distributed. |
This table shows how the process flows from a regular user to the blockchain system. Everyone plays a role, but the final power lies with elected delegates under transparent rules.
Incentives and Rewards in DPoS Moderation
Why Rewards Matter
Moderating content takes time and effort. If people are asked to help but get nothing in return, very few will want to do it. This is why incentives are important. Rewards encourage users to participate honestly, while punishments discourage abuse. With the right balance, DPoS moderation can keep communities active and fair.
Token-Based Incentives
In a DPoS setup, rewards usually come in the form of tokens. For example, if a user flags a harmful post and the delegates agree it really is harmful, that user might earn a small token reward. Delegates who do their job well and make fair calls also get rewarded with tokens for their work.
These tokens aren’t just points that sit in your account. Depending on how the platform is built, they could be used inside the app, traded for other digital assets, or even sold on crypto exchanges. This makes people actually want to get involved in moderation instead of just ignoring it.
Punishment for Abuse
But of course, a fair system also has to deal with abuse. If someone keeps flagging posts for no reason, just to try and earn rewards, they could lose reputation points or even have some tokens taken away. The same thing goes for delegates. If a delegate makes biased or shady decisions, the community can vote them out and replace them.
This mix of rewards and punishments keeps the whole thing in balance. Honest users and delegates get rewarded for helping, while the ones who try to cheat the system end up losing out.
Example: Reward Flow in Action
Imagine a user reports a fake news post. The post is reviewed by delegates, who vote that it is harmful. The smart contract then removes the post, and the reporter automatically gets a reward. If another user falsely reported a normal post just to gain tokens, the delegates would reject the flag. That user might lose reputation points as a warning.
This creates a cycle of trust and responsibility across the platform.
| Action | Outcome for User/Delegate | Reward or Punishment |
| User flags harmful content | Delegates confirm it is harmful | User earns a token reward |
| Delegate votes fairly | Community keeps them in power | Delegate earns tokens and reputation |
| User makes false reports | Delegates reject the flag | User loses tokens or reputation points |
| A delegate makes biased decisions | The community votes them out as moderators | Delegate loses role and rewards |
This table shows how DPoS moderation uses both rewards and penalties to keep the system fair. Everyone has something to gain by being honest, and something to lose if they abuse the system.
Case Studies and Research Insights
Lessons from Existing Decentralized Platforms
Over the past decade, several decentralized social media platforms have been created. Each one shows both the promise and the problems of decentralization.
- Steemit: A blockchain-based platform that rewards users with cryptocurrency for creating and curating content. It uses a token-based system where users vote on posts, and popular posts earn rewards (Ba, Zignani, & Gaito, 2022). This shows how incentives can encourage participation but also highlights risks like vote manipulation.
- Mastodon: A federated social network where users create their own servers (called instances). These servers can connect with each other. Moderation is handled locally by each community, showing how decentralization can give users more control over their space (Bielenberg, Helm, Gentilucci, Stefanescu, & Zhang, 2012).
- Diaspora: Another federated network where users run their own “pods.” This structure makes censorship more difficult but still leaves open questions about how to coordinate moderation across different pods.
These platforms prove that decentralized social media can work, but none of them yet have a scalable, trust-driven moderation system like DPoS could provide.
Academic Research on Blockchain Social Media
Researchers have also studied how blockchain can improve social media governance. For example, a 2024 study introduced a decentralized social media model built on Ethereum and IPFS. The research highlighted how community-driven moderation, combined with incentives, could reduce fake news and censorship problems.
Another 2025 perspective article on decentralized governance stressed that systems like DPoS are essential for preventing power concentration and promoting fairness in digital communities (Esposito, Tse, & Goh, 2025). These findings align with the idea that users want more transparency and accountability in online platforms.
Takeaway
From both practice and research, two lessons stand out:
- Decentralized governance works, but moderation is the hardest problem to solve.
- Incentives and reputation systems are necessary to make users take moderation seriously and to prevent abuse.
By blending these insights, a DPoS-based moderation model could solve long-standing problems that decentralized networks like Mastodon or Steemit still face today.
| Key Feature | Moderation Style | Lesson Learned |
| Rewards for content creation/curation | Token-based voting | Incentives drive engagement but risk manipulation |
| Federated servers (instances) | Local community moderation | Communities want control, but cross-network rules are weak |
| Federated pods | Local moderation | Privacy-friendly, but lacks strong global moderation |
| Ethereum + IPFS prototype | Blockchain + smart contracts | Decentralization strengthens trust and resilience |
| DAO governance study | DPoS-style governance | Voting systems can prevent concentrated power |
This table shows how different projects and research studies point toward the same conclusion: a transparent, incentive-based system like DPoS could provide the missing piece in decentralized content moderation.
Benefits of Using DPoS for Moderation
More Transparency
One of the biggest benefits of using DPoS for content moderation is transparency. On centralized platforms, users rarely know why a post was removed or why another was allowed to stay. The decision process happens behind closed doors.
With DPoS, the moderation rules can be written into smart contracts on the blockchain. These contracts are open for everyone to see, so users know exactly how decisions are made. If a post is flagged and removed, the record of that decision stays on the blockchain. This creates a system where nothing is hidden and accountability is built in.
Faster and Scalable
Another benefit is speed. In decentralized systems, if every user had to vote on every single flagged post, the process would be too slow. DPoS solves this problem by letting users elect a smaller group of delegates.
Because the number of delegates is limited, decisions can be made quickly. At the same time, the delegates remain accountable to the wider community because they can be voted out at any time. This balance makes the system both fast and scalable, even when millions of people use the platform.
Stronger Community Engagement
DPoS also creates stronger community involvement. Instead of relying on paid moderators hired by a company, users directly influence who moderates their content. This gives people more trust in the system because they know they have a voice.
When users feel ownership over the platform, they are more likely to stay active, contribute quality content, and help with moderation. Over time, this makes the community healthier and stronger.
Example of the Benefits in Action
Imagine a platform using DPoS for moderation. A harmful post is flagged. Delegates review and remove it within minutes. The decision is stored on the blockchain, allowing everyone to view the reasoning behind it. The user who flagged it earns a token reward. The community sees that the system is working fairly, and trust in the platform grows.
This is a clear example of how DPoS can combine fairness, speed, and openness to build a social media system that people trust.
Challenges of DPoS in Moderation
Risk of Token Cartels
One major challenge is the risk of token cartels. In DPoS, voting power depends on how many tokens a user owns. This means that if a few people or groups hold a very large number of tokens, they can control the voting process. These large holders might always elect their own delegates, creating a system where only a few voices dominate decisions.
This goes against the idea of decentralization. Instead of being fair and open, the system could slowly become centralized again, with power in the hands of a small group. Researchers studying governance in decentralized systems warn that concentrated power is one of the hardest problems to solve.
ALSO READ: Token Holder Cartels: Can DPoS Stop Concentrated Power Structures?
Risk of Biased Delegates
Even if delegates are elected fairly, there is always the risk of bias or abuse. A delegate could start favoring certain groups or silencing others. Since delegates play a big role in moderation, their personal opinions might affect decisions.
To limit this, platforms need clear smart contract rules and reputation systems. Delegates should know that if they act unfairly, the community can vote them out. Still, this is not always enough to prevent human bias.
Technical Barriers
DPoS-based moderation also faces technical challenges. Smart contracts can make rules transparent, but they have limits. Complex moderation decisions, like detecting sarcasm or cultural context, are hard to put into simple code.
There is also the issue of gas fees on blockchain networks. Every action, such as flagging content or rewarding a reporter, requires a transaction. If fees are high, it could make the system expensive to use.
Example of Challenges in Action
Imagine a platform where three large token holders work together. They control most of the votes and always elect delegates from their group. These delegates start removing posts that criticize them while ignoring harmful posts from their friends. The community loses trust, but smaller token holders lack the power to change the system.
This shows how cartels, bias, and technical limits can weaken the fairness of DPoS moderation if safeguards are not added.
Future of Content Moderation with DPoS
Integration with AI
While DPoS can create a fair voting system for moderation, it can also work together with artificial intelligence (AI). AI tools can scan large amounts of content quickly to detect spam, hate speech, or fake news. Instead of replacing delegates, AI can help them by filtering out obvious, harmful content first.
Delegates can then focus only on the harder cases where context and human judgment are needed. This mix of AI speed and human fairness could make decentralized moderation both fast and reliable.
Building Reputation Systems
Another improvement is the use of reputation systems. In addition to token voting, users and delegates could have reputation scores based on their past actions. For example, a user who often reports harmful posts accurately could gain a higher reputation score. This would make their votes more valuable in the system.
For delegates, a reputation system would show which ones make fair decisions over time. Delegates with strong reputations would be trusted more, while those with poor reputations would struggle to get re-elected. This would reduce the risk of abuse and make the system stronger.
Global Adoption
In the future, decentralized social media platforms using DPoS could spread worldwide. Right now, most decentralized platforms are small compared to giants like Facebook or X. But as people lose trust in centralized moderation, the demand for fairer systems will grow.
Governments, journalists, and online communities may also support platforms where moderation decisions are transparent and public. If DPoS is proven to work at scale, it could become a global standard for fair content moderation.
Example of the Future in Action
Picture a global decentralized platform. A harmful video is uploaded. AI detects it as suspicious and alerts the delegates. Delegates review it, vote to remove it, and the action is stored on the blockchain. The first user who reports it earns a token reward. Other users can see exactly why the video was removed, and trust in the platform increases.
This type of system could finally solve the long-standing problem of balancing free speech, safety, and fairness in social media.
Conclusion
Content moderation is one of the most significant challenges in social media today. Centralized platforms like Facebook and X control what users can say, but their decisions often feel biased, unclear, or unfair. At the same time, leaving platforms completely unmoderated allows fake news, spam, and harmful content to spread unchecked. This shows that a better system is needed, one that balances free speech with safe online spaces.
Decentralized social media gives us a way to share control and build more transparent systems. By using Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), moderation can be done in a community-driven way. Users vote for delegates who make decisions on flagged content, and smart contracts ensure that the rules are open for all to see. Rewards and penalties keep everyone honest, while transparency builds trust across the network.
Looking ahead, combining DPoS with tools like AI and reputation systems could create global platforms that are both safe and democratic. Users would no longer depend on big tech companies to make secret decisions. Instead, they would shape moderation themselves, in a system that is transparent and accountable.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Decentralized Social Media Could Use DPoS
What is DPoS in simple terms?
DPoS stands for Delegated Proof of Stake. It is a blockchain system where users vote for a small group of people, called delegates, to make decisions for the network. It is fast, democratic, and community-driven.
How can DPoS help in content moderation?
DPoS allows users to vote for trusted delegates who act as content moderators. These delegates review flagged posts and decide what stays and what gets removed. The rules are stored in smart contracts, which makes the process transparent.
Is decentralized social media safe?
Yes, decentralized social media can be safe. It gives users more control over data and decisions. By using systems like DPoS, moderation becomes more open and fair, which increases trust.
What are the risks of DPoS in moderation?
The biggest risks are token cartels (large holders controlling votes), biased delegates, and technical challenges like high gas fees. These risks can be reduced with reputation systems, AI tools, and community safeguards.
Which social media platforms are decentralized?
Examples include Steemit, Mastodon, and Diaspora. These platforms are not yet as big as Facebook or X, but they show the future of how social media could work without centralized control.
Glossary of Key Terms
Decentralized Social Media – Platforms where users own and control data instead of one company.
DPoS (Delegated Proof of Stake) – A system where users vote for delegates to make decisions on their behalf.
Smart Contract – A blockchain-based program that runs automatically when rules are met.
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) – A peer-to-peer file system for storing and sharing data without central servers.
Delegate – A person or group elected by users in a DPoS system to validate transactions or moderate content.