How DPoS and Modular Design Make Faster, Flexible, Secure, and Future-Proof Blockchains
Blockchains can be thought of as shared digital ledgers, collectively maintained rather than controlled by a single party. Their integrity depends on one critical principle: consensus, the mechanism by which all participants agree on the validity of data. Without consensus, blockchains would lack both trust and security.
- What Is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)?
- What Are Modular Blockchains?
- How Modular Blockchains Work with DPoS
- Benefits of Using Modular Blockchains with DPoS
- Examples of Modular DPoS Systems
- How Modular DPoS Helps with Blockchain Governance
- Challenges and Risks of Modular DPoS Systems
- Too Many Moving Parts Can Cause Problems
- It’s Harder for Beginners to Understand
- Security Risks Increase with Flexibility
- What the Future Looks Like for DPoS and Modular Blockchains
- More Custom Blockchains for Specific Use Cases
- Better Tools for Community Governance
- Growing Support from Big Projects
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Glossary of Key Terms
Early networks such as Bitcoin relied on Proof of Work (PoW), a highly secure yet energy‑intensive and relatively slow approach. This led to the development of more efficient alternatives like Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). DPoS is particularly notable because it introduces a democratic element, allowing participants to elect representatives who validate transactions and maintain the network.
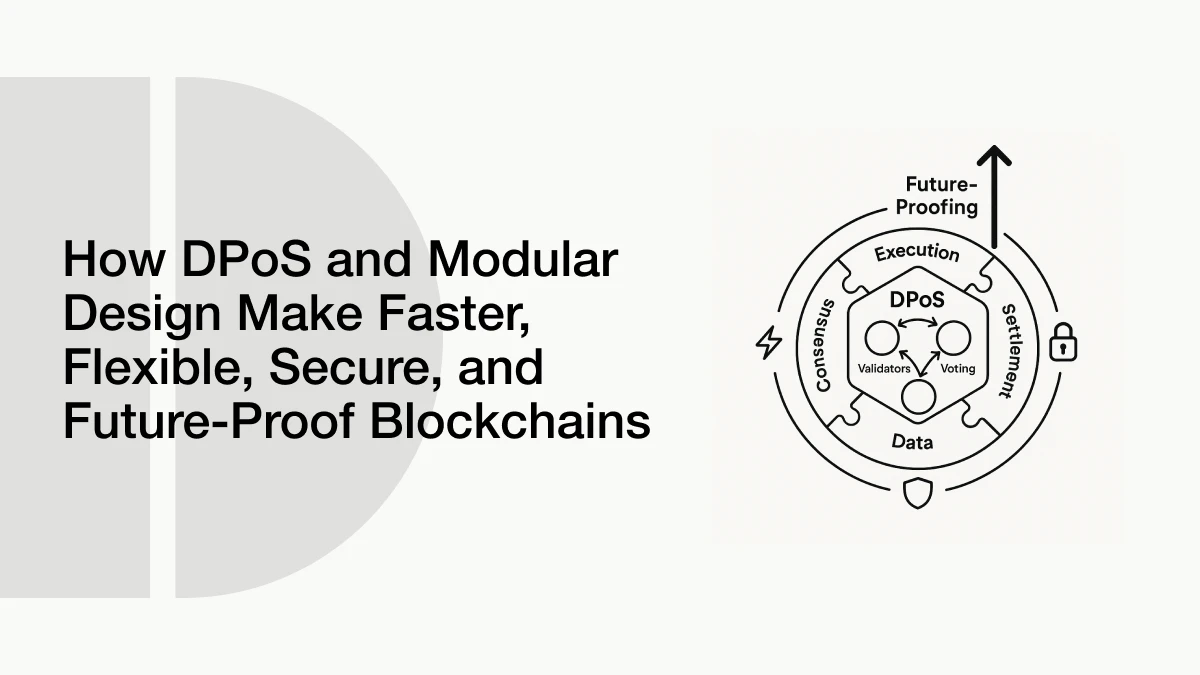
Today, an emerging innovation is reshaping blockchain design: modular blockchains. These architectures separate key functions, such as execution, consensus, and data availability, into distinct, interoperable components, similar to modular building blocks. This article explores how modular blockchains and DPoS governance models can complement one another and potentially redefine the future of decentralized infrastructure.
What Is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)?
Let’s say you are part of a group, and you all want to choose one person to make decisions. Instead of everyone talking at the same time, you vote for someone to speak for you. That’s how DPoS works.
In Delegated Proof of Stake, people who own the blockchain’s token have the right to vote. They vote for a small number of people called delegates. These delegates take care of adding new blocks to the chain and keeping it secure. They are like managers chosen by the community.
Here’s how it works in simple steps:
- You hold tokens in your wallet.
- You use your tokens to vote for a delegate.
- The top delegates get to run the blockchain for a while.
- They take turns adding blocks.
- If a delegate does a bad job, people can stop voting for them.
It is a quicker system that consumes less energy and is community empowered. It is applied to such blockchains as EOS and TRON. However, despite DPoS being superior to older systems, it encounters issues when networks grow extremely large or complex. Enter modular blockchains.
ALSO READ: How NFTs Could Shape the Future of DPoS Governance Through Reputation-Based Voting
What Are Modular Blockchains?
A modular blockchain is similar to assembling a computer out of its components rather than purchasing a pre-assembled version. You select the screen, the processor, the memory, etc. Similarly, a modular blockchain will allow you to select modules in:
- Execution (where the smart contracts or apps run),
- Consensus (where the network agrees on what’s true),
- Data availability (where info is stored and shared),
- Settlement (where final decisions are recorded).
In old blockchains like Ethereum or Bitcoin, all of these jobs were done by one big system. That made the system heavy, slow, and hard to upgrade. With modular architecture, however, one layer has one job. And, since they are isolated, you can upgrade or change one layer without affecting the others.
Here’s a quick example:
- You might have a chain that only focuses on smart contracts (execution).
- You can connect it to a different chain that handles voting and consensus (like DPoS).
- And you can use another service just to store the data and make it available to everyone.
Think of it like ordering food: you get your pizza from one place, your drink from another, and your dessert from somewhere else, all delivered together. That’s what modular blockchains do. Now consider combining DPoS with this kind of flexibility. That’s when things get exciting.
How Modular Blockchains Work with DPoS
At the beginning of blockchains, all was incorporated in a single layer. This implies that all the work, including running apps, processing transactions, and saving data, had to be done by the same part of the system. This was okay initially, but as the network gained popularity, it became slow and cumbersome to operate.
Modular blockchains can come in handy here. They divide the job into small parts instead of constructing everything in one block. So one layer can only deal with data storage, another layer deals with the apps, and a third layer is in charge of reaching consensus, and that is where DPoS comes in.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) works best when it’s in charge of one job: helping everyone in the network agree on what’s true. DPoS does not need to be concerned with other activities, such as smart contracts or data storage, in a modular system. It can simply concentrate on voting, choosing delegates, and confirming blocks. It makes it less time-consuming to handle.
Suppose you have a new blockchain that would like to use DPoS to reach consensus, but has an entirely different layer to run smart contracts. This is possible with a modular design. DPoS can be inserted like a puzzle piece in the system component that is responsible for making agreements and producing blocks. The remaining system can be constructed using other tools, including other teams. This makes it flexible for developers. They can pick and choose what to use. And when one component requires an upgrade in the future, it doesn’t destroy the rest of the system. Thus, modular blockchains not only accommodate DPoS, but they also allow it to shine.
Benefits of Using Modular Blockchains with DPoS
There are numerous large benefits to mixing modular design with DPoS. It assists in addressing some of the issues that were experienced in older blockchain networks, particularly when they became large and slow. The most advantageous is flexibility. With a traditional blockchain, altering a single component of the system implies that you might have to rewrite the entire code base. In a modular blockchain, however, everything is independent. So, say the DPoS layer has to be improved upon, say by adding new voting capabilities or by making changes to the delegate rules, you can do so without touching the execution layer or data layer. That saves time and reduces bugs.
Another mega win is speed. DPoS can operate quickly since it has less work to do, as it only needs to vote and finalize blocks. Meanwhile, it is possible to optimize the other components of the blockchain in isolation. This implies greater transactions per second, a reduction in waiting time, and ease of user experience, despite the large number of individuals using the network simultaneously. It is also less difficult to scale. Each of the layers may be created to grow differently. The consensus layer can be upgraded in case it requires additional delegates or quicker messaging. In case the data layer must be able to store more files or become less expensive, it may change as well. Such a system is similar to a team with each member performing their part, but working towards a common goal.
ALSO READ: How Liquid Staking Derivatives Could Disrupt DPoS Economics (2025 Guide)
Another vital benefit is security. Since each layer has one clear role, developers can check it more easily for bugs or attacks. It’s easier to protect a single-purpose tool than a huge system that does everything at once. And because DPoS has a smaller number of trusted delegates, it’s easier to track and fix any errors or strange behavior fast. Finally, community control becomes more powerful. With a modular design, communities can build the rules they want. They can decide how voting works, how delegates are selected, and even how rewards are shared, all without waiting for permission from a core development team.
In short, modular blockchains make DPoS smarter, faster, and easier to grow. And they open the door for more creative, flexible, and community-led blockchain networks in the future.
Examples of Modular DPoS Systems
Some blockchain projects are already showing how modular design and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) can work well together. These systems separate different parts of the blockchain and let DPoS focus only on the consensus layer. Let’s look at a few popular examples:
| Blockchain Project | Modular Features | DPoS Role |
| EOS | Plans modular updates to separate app logic from core protocol | Uses 21 elected block producers via DPoS |
| Lisk | Focuses on apps built in JavaScript with a separate consensus module | Uses DPoS for voting and delegate selection |
How Modular DPoS Helps with Blockchain Governance
Governance means how decisions are made in a blockchain, such as changing rules, adding features, or fixing problems. In most older blockchains, governance was slow and messy because everything was locked together. If one thing changed, the whole system might break. But modular DPoS makes governance much easier and more flexible. With DPoS, people already vote for delegates who help run the network. But now, with modular design, the rules for that voting can be updated without changing the rest of the system. That means communities can grow and improve their governance models faster.
Let’s say a community wants to:
- Increase the number of delegates from 21 to 30.
- Change the term of each delegate in power.
- Add new rules for how rewards are shared.
In an old system, these changes would need big upgrades or maybe even a complete reset. But in a modular blockchain, you can change just the consensus layer (where DPoS lives), while everything else stays the same. This also allows for testing new voting systems. A community might run one set of DPoS rules on a test chain, get feedback, and then plug it into the main network. This kind of smart upgrade process wasn’t easy before modular systems came along.
Another benefit is clear transparency. Because each part of the blockchain has its own job, it’s easier to track who voted for whom, what changes were made, and how decisions were reached. This builds more trust among users. Finally, modular DPoS helps smaller communities launch their own chains. They don’t need to build everything from scratch. They can take a proven DPoS module, connect it to their app layer, and start testing ideas right away.
So when it comes to governance, modular DPoS gives people more control, better tools, and faster ways to grow their blockchain projects.
Challenges and Risks of Modular DPoS Systems
While modular DPoS systems bring many benefits, they are not perfect. Like any new technology, they come with some challenges. It’s important to understand these risks before jumping in.
Too Many Moving Parts Can Cause Problems
In a modular blockchain, each layer is separate. That sounds good, but sometimes these parts don’t work together smoothly. If the consensus layer (DPoS) isn’t communicating effectively with the data layer or the app layer, users may face delays, bugs, or errors.
Think of it like a food delivery app. The app may work fine, but if the driver (consensus) is slow or the restaurant (execution layer) is late, your order won’t arrive on time. Every part must stay in sync for things to run smoothly. This is harder in modular systems because everything is more complex. Developers must test the system more often to ensure all parts work together smoothly.
It’s Harder for Beginners to Understand
One reason why DPoS became popular is that it’s easier to understand than Proof of Work. But when you mix DPoS with modular blockchain layers, things can get confusing again.
People may not know:
- Which part controls what?
- Where to report issues?
- How does voting connect to real decisions?
This confusion can lead to fewer people getting involved, which weakens the whole point of DPoS, community-driven control. If only a few people understand the system, they might end up controlling it too much. So, education and good documentation become very important in modular systems.
Security Risks Increase with Flexibility
One big worry is security. In a regular blockchain, all parts are protected by the same security model. But in a modular blockchain, each layer has its own security system. If one layer is weak, it can open the door to attacks. For example, if the DPoS consensus layer is strong but the data availability layer is not, attackers might hide or fake information. This can lead to double-spending or other fraud.
Also, since delegates are chosen by voting, there’s always a risk that someone with a lot of tokens might control the vote. This isn’t new in DPoS, but when mixed with modular design, it might get harder to spot or fix. That’s why every layer needs strong security, and they must all work together like a team.
ALSO READ: Is This the Future of Blockchain? The Impact of AI Bots on Voting in DPoS Systems
What the Future Looks Like for DPoS and Modular Blockchains
The world of blockchain is changing fast. And modular DPoS systems are a big part of that change. More developers are now building flexible networks that can be easily updated and improved. At the same time, people still want secure and fast consensus, which is what DPoS is good at.
More Custom Blockchains for Specific Use Cases
In the future, we may see many small blockchains built just for one job, like voting, saving files, or running games. These chains will not need to build everything from scratch. Instead, they can connect to a modular DPoS consensus layer to ensure safety and decentralization.
This makes blockchain more open to creators, startups, and even local communities. Anyone with a good idea can build a working system without millions of dollars or a huge tech team.
Better Tools for Community Governance
Modular DPoS also helps grow better systems for on-chain voting and decisions. With clearer separation between layers, developers can build strong tools for community feedback, rules, and proposals.
This will make blockchain governance fairer, more active, and more trusted. Communities will be able to:
- Update how delegates are picked
- Change reward systems quickly
- Try new voting models safely before going live
All of this leads to stronger, healthier blockchains.
Growing Support from Big Projects
Some of the biggest names in blockchain, like Cosmos (ATOM) and Polkadot (DOT), are already working with modular systems. Newer projects are being built with this idea from day one. This shows that modular DPoS isn’t just an experiment anymore. It’s becoming the new normal.
As more tools, SDKs, and documentation become available, modular DPoS networks will become easier to launch and manage. That means the world will see more competition, more innovation, and better user experiences for everyone, from app developers to regular users.
Conclusion
Modular blockchains and DPoS are a powerful combination. DPoS is fast, democratic, and energy efficient. Modular design introduces flexibility, ease of upgrade, and improved attention to each component of the system. Combined, they make blockchains simpler to construct, scale, and control. Previously, creating a blockchain was similar to constructing a gigantic machine in which all components needed to be integrated. With modular DPoS, it is now possible to construct blockchains more like modern computers, where various components can be swapped, enhanced, or discarded without needing to rebuild the entire system.
This implies that blockchain technology is expanding. It is becoming more professional, more user-friendly, and better equipped to solve practical issues. As an investor, developer, or even someone who simply wants to see what the future holds, you should watch the modular DPoS systems. As more blockchains switch to modular layers, we’ll see faster apps, smarter voting, and better tools for communities to run their own digital worlds. And that’s a future worth building.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a modular blockchain?
A modular blockchain breaks its system into different parts, like voting, running apps, and storing data. Each part is separate and can work on its own. This makes it easier to upgrade, fix, or improve without touching the whole system.
How does DPoS work in simple terms?
DPoS lets token holders vote for people called delegates. These delegates help run the network by confirming transactions and creating new blocks. It’s faster and uses less energy than older systems like Proof of Work.
Why combine DPoS with modular blockchains?
Combining DPoS with modular design makes the network faster, safer, and easier to upgrade. DPoS handles just the voting part, while other parts do their own jobs. This keeps everything running smoothly.
Is DPoS better than Proof of Work?
For many use cases, yes. DPoS is faster, more energy-efficient, and easier to scale. But it needs honest delegates and active community voters to work well.
What are some real examples of modular DPoS blockchains?
Cosmos and Polkadot use modular designs with DPoS-like voting systems. EOS and Lisk also use DPoS and are moving toward modular upgrades.
Glossary of Key Terms
Blockchain
A digital system that stores data in blocks and links them together. It’s secure, public, and not controlled by one person.
Consensus
An agreement between all participants in a blockchain about what data is true.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
A voting system where users choose delegates to manage the blockchain and add new blocks.
Modular Blockchain
A blockchain that splits its work into different layers or parts, each with a specific job.
Validator / Delegate
A person or node is elected to help keep the blockchain running and validate transactions.
Governance
The way decisions are made in a blockchain includes rule changes, upgrades, and voting.
Execution Layer
The part of the blockchain that runs smart contracts and apps.
Consensus Layer
The part that helps everyone agree on what’s true in the network.
Data Availability Layer
The part that stores and shares blockchain data is accessible to everyone.
Smart Contract
A program that runs automatically when specific rules are met. Often used in decentralized apps.