How DPoS Validator-as-a-Service Will Shape the Next Staking Trend in 2025 and Beyond
Staking has become one of the most popular ways to earn rewards in the crypto industry. Instead of just holding coins, users can lock them in a blockchain network and get paid for helping to keep the system secure. This idea has grown quickly in the last few years and is now a key part of many blockchains.
- What is DPoS and How Does It Work?
- Why Staking is Growing in 2025
- Comparing Consensus Mechanisms
- What is Validator-as-a-Service (VaaS)?
- The Basic Idea of VaaS
- Why People Use VaaS
- Example of VaaS in Action
- What Are the Benefits of Validator-as-a-Service in DPoS?
- Easier Access for Everyone
- Stronger Network Security
- Reduced Risk of Mistakes
- Passive Income Made Simple
- Self-Running a Validator vs. Using a Validator-as-a-Service
- Risks and Challenges of Validator-as-a-Service
- Centralization Concerns
- Trusting Third-Party Services
- Fees and Profit Sharing
- Regulatory Uncertainty
- Example of Past Challenges
- DPoS Validator-as-a-Service vs. Traditional Staking Pools
- How Staking Pools Work
- How Validator-as-a-Service is Different
- Which One is Better?
- Staking Pools vs. Validator-as-a-Service
- Industries and Use Cases Benefiting from VaaS
- Retail Investors and Passive Income
- Institutions and Enterprises
- Developers and Startups
- Emerging Sectors: DeFi, Gaming, and Tokenized Assets
- Who Benefits from Validator-as-a-Service?
- How to Choose the Right Validator-as-a-Service
- Reputation and Track Record
- Security Measures
- Fee Structure and Transparency
- Community Governance and Support
- Key Factors for Choosing a VaaS Provider
- Future of Validator-as-a-Service in DPoS
- Market Growth Predictions
- Making Staking Mainstream
- Role of AI and Automation
- Global Regulation and Adoption
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Glossary of Key Terms
One of the biggest shifts in staking is the rise of Delegated Proof of Stake, also called DPoS. In this system, people do not need to run complex computers to validate blocks. Rather, they can delegate special participants (referred to as validators or delegates) to do the work on their behalf. This aims to make blockchain more accessible, equitable, and faster for all. DPoS has already been used in well-known projects like EOS and Tron, showing that it can scale better than older methods like Proof of Work.
With the expansion of the industry, a new tendency is beginning to emerge. It is referred to as Validator-as-a-Service (VaaS). This concept allows businesses or service providers to operate validators on behalf of users who prefer staking but lack the time, resources, or expertise. These providers open up staking by offering validator services, also bringing it to the masses. Just like cloud services made computing easier, Validator-as-a-Service could make staking mainstream in the coming years.
This blog will explore what DPoS is, why Validator-as-a-Service matters, and how it could change the future of the staking industry. It will look at the benefits, risks, and opportunities, and explain everything in simple terms. By the end, you will understand why many experts believe Validator-as-a-Service is the next big staking trend and how you can benefit from it.
What is DPoS and How Does It Work?
Delegated Proof of Stake, or DPoS, is a special type of blockchain system. It was first introduced in 2013 by Daniel Larimer, who wanted to build something faster and easier than older blockchain models. DPoS is a different version of Proof of Stake (PoS), but it adds a new layer of democracy to the process.
ALSO READ: Breaking Barriers: Why DPoS Could Be the Future of Borderless Credit and Microfinance
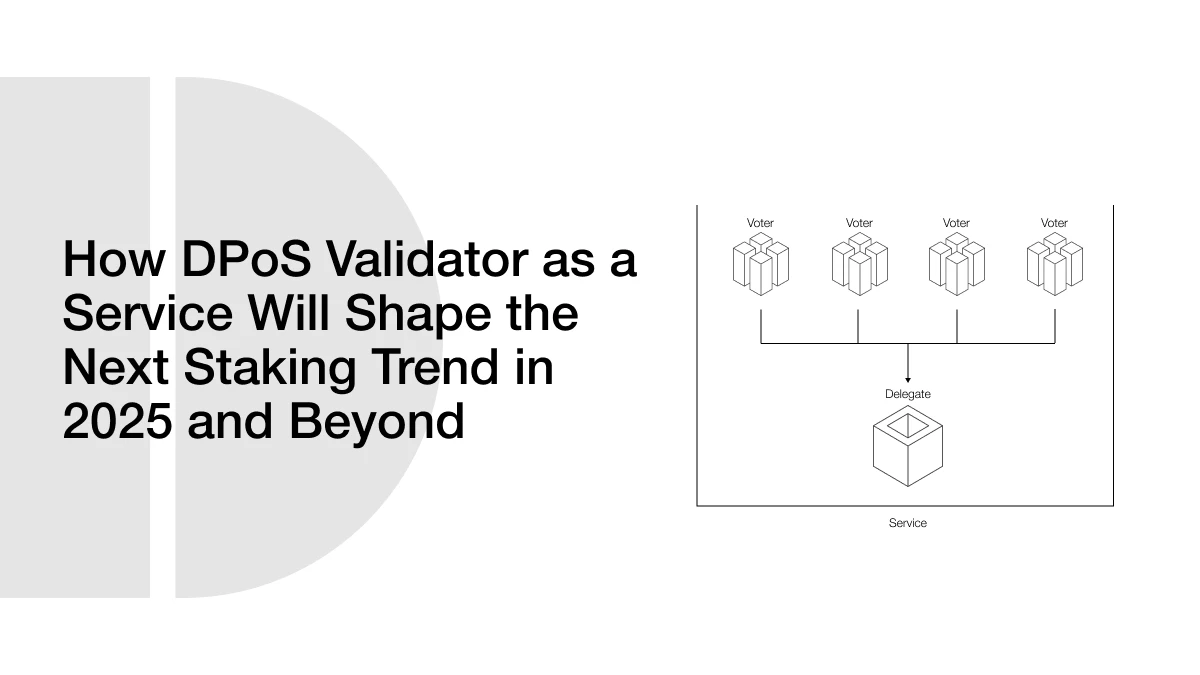
In a normal Proof of Stake system, people who lock their coins (stake) may be chosen to create new blocks and confirm transactions. But DPoS changes this. Instead of everyone competing to validate, the community votes for a small group of validators. These validators are also called “delegates” or “block producers.” Only these selected few have the job of verifying transactions and creating new blocks.
The voting system makes DPoS more democratic and efficient. If a validator does a good job, people keep voting for them. If they act dishonestly or make mistakes, voters can remove them and pick someone else. This creates accountability. It also keeps the network fast, since only a limited number of validators are working at a time.
Another important detail is rewards. When a validator creates a block, they earn rewards such as transaction fees or new tokens. Many validators share a part of these rewards with the people who voted for them. This way, both validators and regular users benefit from the system. For example, in networks like Tron or EOS, delegators get passive income without running their own technical setups.
Overall, DPoS works like a digital democracy. Users still have power through voting, but they don’t need to do the hard technical work. This balance between speed and fairness is what makes DPoS one of the most popular consensus systems today.
Why Staking is Growing in 2025
Staking has ceased to be an additional activity in crypto and has become one of the largest trends in the industry. In 2025, billions of dollars have already been locked in the staking networks, and it continues to increase every month. This is because it is simple; people want safer methods of earning rewards without the anxiety of trading.
Staking lets users earn passive income. Instead of selling coins or watching prices all day, they can lock tokens in a network and collect rewards. This approach has made staking attractive not only for small investors but also for large institutions. For many, it feels similar to earning interest in a savings account, but with higher returns.
The other factor that has led to the increased growth of staking is due to blockchain upgrades. Many networks are leaving Proof of Work, which uses much energy, and moving to Proof of Stake or Delegated Proof of Stake. These systems are faster, cheaper, and far more environmentally friendly. As more projects implement these models, staking opportunities continue to increase.
Staking also supports the security and growth of blockchain systems. When people lock their tokens, they make it harder for hackers or attackers to take over the network. This is why staking rewards are given. They are not only a gift to users but also a tool to keep the network safe and active.
To understand how DPoS compares to other methods, let’s look at the main differences.
Comparing Consensus Mechanisms
| Feature | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) | Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) |
| Energy Use | Very High | Low | Low |
| Speed of Transactions | Slow (minutes) | Faster (seconds) | Very Fast (a few seconds) |
| Who Creates Blocks | Miners with computers | Stakers with coins | Voted Validators (Delegates) |
| User Involvement | None after mining | Must stake tokens | Must stake and vote |
| Risk of Centralization | Mining pools | Wealthy stakers | Small group of validators |
This shows why DPoS and staking are rising. They use less energy, process faster, and give users more chances to participate. In 2025, these advantages are pushing staking forward as one of the strongest parts of the blockchain economy.
What is Validator-as-a-Service (VaaS)?
Validator-as-a-Service, or VaaS, is a new idea that is becoming very popular in the staking world. It is designed for people who want to earn staking rewards but don’t want to run complicated validator nodes by themselves.
The Basic Idea of VaaS
Running a validator in a DPoS network is not easy. You need strong servers, a constant internet connection, and advanced technical skills. If the validator goes offline or makes mistakes, you can lose rewards. Many everyday users do not have the time or the tools for this.
This is where Validator-as-a-Service comes in. Instead of setting up a validator on your own, you pay or partner with a professional company. They run the validator for you. You still get staking rewards, but the company makes sure everything works smoothly.
Why People Use VaaS
People use VaaS because it removes stress and makes staking more accessible. Small investors who only have a few tokens can join safely. Large investors or institutions also use VaaS because they want reliable performance and security. With professional operators, they don’t need to worry about downtime or technical failures.
Example of VaaS in Action
Imagine you have tokens in a DPoS network like EOS. Instead of running your own validator, you choose a service provider that already has strong infrastructure. You delegate your tokens, and they take care of validation. In return, they share the rewards with you, sometimes charging a small service fee.
This model works much like cloud computing. Just as cloud services made it easier for businesses to use advanced technology without owning servers, VaaS makes it easier for crypto users to stake without owning validator hardware. Experts believe this will help staking grow even faster in the coming years.
What Are the Benefits of Validator-as-a-Service in DPoS?
Validator-as-a-Service is not just a trend. It solves many problems that people face when they want to stake in DPoS networks. By letting professionals handle validator nodes, this model brings several benefits to both small investors and large institutions.
Easier Access for Everyone
In traditional staking, only people with technical knowledge or large amounts of money could set up validators. With VaaS, anyone can take part. Service providers lower the barrier by doing the hard work, while users simply delegate their tokens. This makes staking more open and inclusive, which is suitable for both the blockchain and the users.
Stronger Network Security
When more people can join through VaaS, the blockchain becomes stronger. A bigger pool of delegators supports more validators, making it harder for any single group to control the system. This extra participation helps maintain decentralization and prevents attacks. Networks like Tron and EOS have already shown that higher voter turnout leads to healthier systems.
Reduced Risk of Mistakes
Running your own validator comes with risks. If your node goes offline or is set up incorrectly, you may lose rewards. In some blockchains, you can even be penalized. VaaS providers run advanced infrastructure, often with backup systems and 24/7 monitoring. This reduces errors and ensures steady rewards for users.
Passive Income Made Simple
For many investors, the main reason to stake is to earn passive income. Validator-as-a-Service makes this as simple as possible. Instead of learning technical steps, users just pick a provider and delegate. They can enjoy steady returns without worrying about uptime, software updates, or hardware failures.
Self-Running a Validator vs. Using a Validator-as-a-Service
| Feature | Self-Run Validator | Validator-as-a-Service (VaaS) |
| Technical Knowledge | High (server setup, coding, security) | Low (provider handles it) |
| Hardware Cost | Expensive (servers, internet, backups) | None for user |
| Risk of Downtime | High if managed poorly | Very Low (professional setups) |
| Reward Sharing | 100% if successful | Shared (after provider’s fee) |
| Accessibility | Limited to experts | Open to everyone |
| Convenience | Time-consuming | Easy and stress-free |
Validator-as-a-Service gives everyday users the chance to enjoy the benefits of staking without the stress. At the same time, it provides institutions with a professional-grade solution for managing large amounts of tokens. This combination is why experts call it the next big trend in staking.
Risks and Challenges of Validator-as-a-Service
Even though Validator-as-a-Service makes staking easier, it is not perfect. Like any new model, it comes with risks that both investors and developers should understand before joining.
Centralization Concerns
One of the biggest risks in DPoS is centralization. Since only a few validators are active at any time, there is always a chance that power could gather in the hands of a few providers. If most people delegate to the same VaaS company, that company could have too much control. This goes against the goal of decentralization in blockchain.
Trusting Third-Party Services
With VaaS, you are putting trust in a service provider. If the provider is dishonest or not transparent, they could misuse their position. For example, they might keep more rewards than promised or fail to deliver secure services. Unlike running your own validator, you don’t have complete control, which can make some investors nervous.
Fees and Profit Sharing
Using a Validator-as-a-Service is not free. Providers usually charge fees or keep a part of the staking rewards. While this is fair because they provide the infrastructure, it reduces the final income for delegators. If fees are too high, small investors may not find the rewards attractive.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Staking is still a gray area in many countries. Some governments see staking rewards as income, while others are still deciding how to regulate it. Validator-as-a-Service providers may face future rules, taxes, or licensing requirements. If laws become strict, this could affect how easy it is for everyday users to stake through services.
Example of Past Challenges
Previously, there has been backlash on some staking services when they were hacked or when providers have not been able to provide rewards on time. These experiences show the relevance of selecting trusted providers. Investors should keep in mind that although VaaS can cut the technical workload, it is necessary to choose reliable companies carefully.
Validator-as-a-Service is potent, and these dangers serve as a reminder that users should research before making a decision to join. The future of staking will rely on how much a compromise between convenience and decentralization is achieved.
DPoS Validator-as-a-Service vs. Traditional Staking Pools
Many individuals confuse Validator-as-a-Service and staking pools, yet they are not interchangeable. The two allow users to receive rewards without operating their own validators, but their functionality and the degree of control they provide are highly dissimilar.
How Staking Pools Work
A staking pool is when a group of users combine their tokens to increase the chance of earning rewards. The pool then shares the rewards among the participants. Pools are popular in Proof of Stake systems like Cardano or Ethereum 2.0, where staking solo may be tricky for smaller investors.
How Validator-as-a-Service is Different
Validator-as-a-Service focuses on running professional validator nodes on behalf of users. Instead of just joining a group, you are delegating your tokens to a company or provider that takes care of everything. VaaS is usually built for Delegated Proof of Stake systems, where voting and validator quality are more significant.
Which One is Better?
The choice depends on the user. Staking pools are simple and usually have low fees, but they can be less professional and may not guarantee high uptime. Validator-as-a-Service costs a bit more, but it offers enterprise-grade security, 24/7 monitoring, and professional reliability.
Staking Pools vs. Validator-as-a-Service
| Feature | Staking Pools | Validator-as-a-Service (VaaS) |
| Setup Needed | None for users | None for users |
| Who Runs It | Community or small group | Professional companies or providers |
| Focus Network Type | PoS networks (Cardano, Ethereum) | DPoS networks (EOS, Tron, BitShares) |
| Reward Sharing | Shared among all pool members | Shared after the provider’s fee |
| Reliability | Depends on the pool manager | Very High (enterprise infrastructure) |
| Control for Users | Low, just join and wait | Medium, delegate, and vote |
| Best For | Small investors looking for easy access | Retail and institutions, wanting security and uptime |
Industries and Use Cases Benefiting from VaaS
Validator-as-a-Service is not only useful for individual investors. It is also becoming important for many industries and organizations. By removing technical barriers, VaaS is opening new ways to use blockchain in finance, gaming, and other sectors.
ALSO READ: How Stablecoins Strengthen Liquidity, Speed, and Stability in DPoS Networks
Retail Investors and Passive Income
One of the biggest groups benefiting from VaaS is everyday investors. Many people want to earn rewards from their crypto but don’t know how to run a validator. VaaS gives them a simple path. They can delegate tokens and start earning without learning technical skills. This helps more people join the staking economy and increases overall network activity.
Institutions and Enterprises
Large companies, hedge funds, and even banks are also turning to Validator-as-a-Service. For them, security and compliance are the most important factors. Running their own validators would require time, money, and expertise. With VaaS, they can stake large amounts safely through professional providers. Some blockchain service companies even offer insurance, audits, and guaranteed uptime for enterprise clients.
Developers and Startups
For developers, running validator nodes can take attention away from building products. VaaS solves this problem by letting teams focus on creating dApps, DeFi tools, or Web3 projects, while professionals handle validation. This way, new blockchain projects can grow faster without worrying about node operations.
Emerging Sectors: DeFi, Gaming, and Tokenized Assets
VaaS is also becoming a trend in newer industries like decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain gaming. In DeFi, liquidity providers and token holders can delegate tokens to validators for extra yield. In gaming, some projects let players stake in-game tokens through validators to earn rewards or unlock features. Tokenized assets, like real estate or digital collectibles, also benefit because validators secure transactions while users earn income.
Who Benefits from Validator-as-a-Service?
| Sector/Group | How They Benefit from VaaS | Example Use Case |
| Retail Investors | Easy passive income | Small investor staking Tron tokens |
| Institutions | Security, compliance, uptime | Hedge fund using VaaS provider for EOS |
| Developers/Startups | Focus on building products | dApp project delegating validation |
| DeFi & Gaming | Extra yield and features | Game tokens staked with a validator |
| Tokenized Assets | Secured ownership transfers | Real estate on blockchain using validators |
Validator-as-a-Service makes staking practical for everyone, from small investors to global companies. This wide adoption is one reason why experts believe it will be a major part of the next wave of blockchain growth.
How to Choose the Right Validator-as-a-Service
Not all Validator-as-a-Service providers are the same. Since your rewards and security depend on the service you choose, it’s important to know what to look for before delegating your tokens.
Reputation and Track Record
The first thing to check is the provider’s reputation. A good VaaS company should have a history of reliable performance. Look for providers who are trusted by the community, have a long-standing reputation, and have no history of dishonest practices. Many blockchains also show uptime and past performance of validators, which helps users make informed choices.
Security Measures
Security is one of the most important factors in staking. A reliable provider should have robust security measures like backup servers, monitoring systems, and firewalls. Some even carry out independent audits to prove their systems are safe. If a validator is not secure, users risk losing rewards or even facing penalties in some blockchains.
Fee Structure and Transparency
Most Validator-as-a-Service providers charge fees, usually by taking a small percentage of rewards. This is normal, but the fee should be fair and transparent. Some providers may offer lower fees to attract delegators, while others charge more but provide premium services like insurance or advanced analytics. Transparency is key; users should always know how much they are paying and what they are getting.
Community Governance and Support
Another factor is how well the provider connects with its community. Some validators are active in governance, meaning they vote on proposals and help shape the future of the blockchain. Others simply provide technical services. Depending on your goals, you may prefer a provider that takes part in governance. Customer support is also important; the best providers offer help through chat, email, or forums.
Key Factors for Choosing a VaaS Provider
| Factor | What to Look For | Why It Matters |
| Reputation & Track Record | History of uptime and honesty | Shows reliability |
| Security | Backup servers, audits, monitoring | Protects your rewards |
| Fee Structure | Clear and fair percentages | Ensures transparency |
| Community Involvement | Active in governance, open communication | Supports decentralization |
| Customer Support | Quick responses and guidance | Helps delegators feel safe |
Choosing the right Validator-as-a-Service is like choosing a business partner. The right one can give you steady rewards and peace of mind, while the wrong one can lead to losses and stress. By focusing on these factors, users can maximize both safety and profit.
Future of Validator-as-a-Service in DPoS
Validator-as-a-Service is still a young idea, but it is growing fast. Many experts believe it will shape the future of staking, especially in Delegated Proof of Stake networks.
Market Growth Predictions
In 2025, staking already holds billions of dollars in locked value. As more people look for safe and simple ways to earn passive income, Validator-as-a-Service will attract even more users. Reports suggest that professional staking services could double in size over the next few years as institutions and retail investors both join in.
Making Staking Mainstream
For many people, staking still feels too technical. But with VaaS, users do not need to run nodes or study blockchain code. They can join with just a few clicks. This simplicity could make staking as common as online banking. Just as cloud computing changed the way businesses use technology, Validator-as-a-Service could change how people stake tokens worldwide.
Role of AI and Automation
Another trend is the use of artificial intelligence and automation in validator services. AI can help predict network risks, adjust settings for better performance, and even detect threats before they happen. Automated systems can keep validators online 24/7 without human errors. This will make Validator-as-a-Service even more reliable in the future.
Global Regulation and Adoption
Governments are starting to focus on staking. Clear rules will likely appear in the next few years. While this may add some restrictions, it could also make Validator-as-a-Service safer by protecting users from dishonest providers. Once regulations are clearer, more banks, funds, and enterprises may feel comfortable staking through VaaS providers.
ALSO READ: Data Processing with DPoS and Edge Computing: Blockchain’s Future Looks Bright
Final Thoughts
Delegated Proof of Stake has already proven itself as a faster, greener, and more democratic way of running blockchains. But the rise of Validator-as-a-Service takes it one step further by lowering the barriers for everyone. Whether it’s a small investor looking for passive income or a large institution needing security, VaaS makes staking simpler, safer, and more accessible. It brings professional-level infrastructure into the hands of everyday users without requiring them to be tech experts.
As the staking industry grows in 2025 and beyond, Validator-as-a-Service is set to become one of its biggest trends. It is not just about convenience; it is about scaling blockchain adoption worldwide. By combining efficiency, security, and accessibility, VaaS could become the standard entry point for staking in Delegated Proof of Stake systems. For users, this means new opportunities. For the industry, it means faster growth and more trust in blockchain as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Validator-as-a-Service in DPoS?
It is a service where professional providers run validator nodes on behalf of users, so delegators can earn staking rewards without managing hardware or software themselves. - Is Validator-as-a-Service safe for small investors?
Yes, it can be safe if you choose a trusted provider with good uptime, strong security, and fair fees. - How do VaaS providers earn money?
They take a small percentage of the staking rewards as a fee for running the validator infrastructure. - What are the risks of using Validator-as-a-Service?
The main risks are centralization, trust in third parties, and fees. Users must also be mindful of future regulations. - Will VaaS replace self-staking?
Not completely. Some users will still prefer running their own validators, but VaaS will make staking accessible to a much larger group of people.
Glossary of Key Terms
- DPoS (Delegated Proof of Stake): A consensus system where users vote for validators to confirm transactions.
- Validator: A node that confirms transactions and creates new blocks.
- Delegator: A user who stakes tokens and votes for validators.
- Staking Rewards: Earnings given to users for helping secure the network.
- Validator-as-a-Service (VaaS): A professional service that runs validator nodes for users.