How to Build a Custom DPoS Chain Using Cosmos SDK
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) has emerged as a favored consensus method for blockchain networks emphasizing scalability, energy efficiency, and governance participation. The Cosmos SDK provides a robust foundation for developing customized DPoS blockchains that can be tailored to specific use cases, enabling the management of consensus mechanisms, validator relationships, and financial structures. The SDK is commonly utilized in both research and production settings.
- Why Use Cosmos SDK for a DPoS Chain
- Steps to Establish a DPoS Framework
- How to Build a Custom DPoS Chain Using Cosmos SDK – Developer Toolkit
- How Tendermint Supports DPoS
- Connecting Modules and Enabling Interoperability
- Security and Code Reliability
- Designing a Sustainable Token Economy
- Testing and Deploying the Network
- Real-World DPoS Chains Built with Cosmos SDK
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Glossary of Key Terms
- References
Researchers examining modular blockchain frameworks have recognized Cosmos SDK as one of the most adaptable tools for initiating independent chains with reliable performance and rapid finality. Its connection with Tendermint, an engine for Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus, guarantees strong validation and enables developers to craft distinctive application logic. This makes Cosmos SDK a suitable choice for those designing DPoS systems that are efficient, secure, and interoperable with other blockchains (Surmont et al., 2023).
Why Use Cosmos SDK for a DPoS Chain
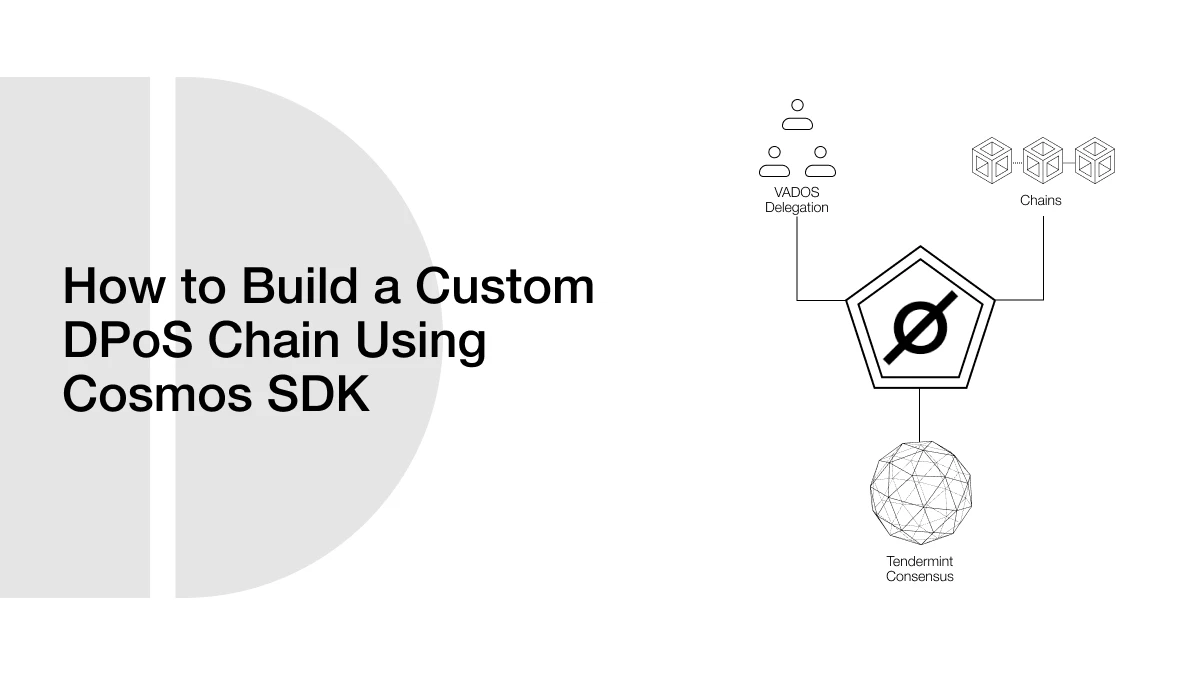
The Cosmos SDK is a flexible framework that allows developers to build blockchains with customized features while relying on a strong core infrastructure. The design separates the application layer from the networking and consensus layers. This division facilitates the creation of customized modules that seamlessly integrate with essential systems while maintaining security.
Tendermint Core manages consensus for networks within the Cosmos ecosystem. It ensures that every node concurs on the identical collection of blocks, regardless of whether some participants are untrustworthy or experience failures. This is vital in DPoS systems, where a chosen group of validators oversees the management of block creation. The governance, staking, and slashing features of the SDK offer essential capabilities for conducting the validator election process securely and transparently.
Moreover, Cosmos enables interaction among blockchains via the IBC protocol. A tailored DPoS chain created with the SDK can link to multiple blockchains within the Cosmos ecosystem, enhancing its functionalities and value prospects.
Steps to Establish a DPoS Framework
A DPoS system relies on token holders choosing a limited set of validators to create blocks and secure the blockchain. This voting power is typically determined by the number of tokens held or allocated. Validators with the highest support are selected to validate transactions, and they allocate block rewards to their delegators. To execute this in Cosmos, developers start with the built-in staking module.
This module enables delegation, bonding periods, penalties for violations, and reward distribution. It can be customized to accommodate the necessary number of validators, the voting mechanism, or the incentive standards. In a DPoS framework, the set of validators is adaptable and should reflect the most recent voting results. This shows that changes in delegation directly influence who supports the network.
Developers can modify the staking module or add new logic to enable validator rotation, set voting thresholds, or conduct elections based on time. The governance module allows the community to vote on protocol updates or changes to validator configurations.
How to Build a Custom DPoS Chain Using Cosmos SDK – Developer Toolkit
| Parameter | Default Value | Customisable? | Impact |
| Max Validators | 100 | Yes | Controls decentralization |
| Unbonding Time | 21 days | Yes | Affects liquidity + security |
| Inflation Rate | 7% | Yes | Impacts staking ROI and tokenomics |
How Tendermint Supports DPoS
Tendermint provides instant finality and reliability, making it suitable for DPoS networks that depend on a small group of validators operating consistently. Validators employ a private key to sign blocks, and the network reaches consensus when more than two-thirds of the voting power concurs.
In a customized DPoS chain, the validator set must be regularly refreshed to reflect changes in delegation. Tendermint enables validator modifications with every block, based on the staking condition. Developers must ensure that these updates are impactful and based on solid reasoning. Poor handling of validator updates can cause instability; thus, it is vital to extensively test state transitions in the staking module before deployment.
Cosmos SDK gives full control over how validators are selected, changed, or removed. This allows builders to enforce policies such as maximum validator count or minimum stake requirements.
Connecting Modules and Enabling Interoperability
Each chain based on the Cosmos SDK is made up of modules. This encompasses vital elements for banking operations, staking, governance, and distribution, along with personalized modules created by the blockchain developers. Modules are crafted for composability, allowing them to merge effortlessly without altering fundamental logic.
Additional modules such as CosmWasm or IBC can be integrated to facilitate smart contracts or assist in cross-chain token transfers. CosmWasm provides smart contract capabilities, whereas IBC allows the chain to interact and transfer assets across different blockchains.
Developers integrate all required modules into the main configuration of the application. They should explain how modules interact via messages, manage transaction validation, and react to alterations in state. Effective integration guarantees that staking, rewards, governance, and token ecosystems operate in harmony.
Security and Code Reliability
Safety is a significant issue when developing DPoS systems. Every node has to handle transactions in the identical sequence and achieve the same outcome. A study conducted in 2023 on Cosmos-based chains emphasized that non-deterministic logic, where code acts inconsistently across machines, can disrupt consensus and result in forks or failures (Surmont et al., 2023).
To mitigate these risks, developers ought to adhere to best practices in software creation. This encompasses utilizing automated testing tools, performing static analysis to detect logical errors, and conducting integration tests that replicate real-world scenarios.
Cosmos SDK likewise enables local testnets and upgrade modules, permitting developers to conduct trial deployments prior to launching on the mainnet. The mechanisms for staking, validator selection, and slashing need to be examined thoroughly. Slashing rules should be stable and foreseeable to prevent unjust penalties or validator turnover.
Designing a Sustainable Token Economy
In a DPoS blockchain, the reward system must be carefully designed to ensure a balance among validator incentives, inflation, and general network participation. Most Cosmos SDK chains use inflationary rewards, meaning that new tokens are created gradually and distributed to validators and delegators.
ALSO READ: Staking in DPoS Networks: Know All About Risks, Rewards, and ROI
High inflation can reduce the token’s worth. Lack of adequate incentives may not motivate validators to safeguard the chain. Chains can adjust inflation rates instantly based on staking ratios or apply predetermined schedules tied to governance votes.
Bonding and nonbonding intervals are equally significant. An extended unbonding period prevents quick token withdrawals, contributing to enhanced security. Nonetheless, it could limit liquidity for users.
Research in staking design emphasizes the need for decentralization and validator diversity. Chains that concentrate voting power in a few validators become more vulnerable to attacks or censorship (Oderbolz et al., 2024).
Testing and Deploying the Network
Prior to initiating a tailored DPoS chain, developers should rigorously assess each component of the system. This comprises unit tests for separate modules, integration tests for inter-module interactions, and network tests utilizing actual validator nodes.
After testing is finished, the chain can be initiated with a genesis file. This document holds the network’s initial configuration, encompassing token balances, validator keys, and module settings. Validators and delegators subsequently connect to the network and start engaging in block generation and governance.
The governance module can manage upgrades and alterations to parameters. This prevents hard forks and enables the chain to evolve gradually with community contributions.
Real-World DPoS Chains Built with Cosmos SDK
| Blockchain | Focus Area | Key Features |
| Osmosis | Decentralized AMM (Automated Market Maker) | Governance-enabled upgrades, customizable DEX logic |
| Evmos | Ethereum Compatibility | EVM support, bridges the Cosmos and Ethereum ecosystems |
| Regen Network | Sustainability & Ecological Data | Blockchain for environmental asset tracking and regeneration |
Conclusion
Creating a tailored DPoS blockchain with the Cosmos SDK is an effective method to establish a blockchain that aligns with distinct governance, staking, and performance objectives. The modular architecture of the SDK and the Swift consensus engine from Tendermint provide developers with complete design control while guaranteeing reliability and compatibility across chains.
For a successful DPoS chain, developers need to grasp not just the technical components but also the economic and governance dynamics that affect user actions. By implementing robust testing methods and careful design, Cosmos-based chains can attain both efficiency and decentralization.
Cosmos SDK provides developers and researchers with an efficient platform to experiment with new concepts and create scalable, tailored blockchains that work effortlessly with larger ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can I change the validator count after the chain launch?
Yes, through on-chain governance proposals using the `gov` module.
- How do I ensure the validator set updates safely?
Tendermint updates validator sets block-by-block. Ensure slashing and staking transitions are deterministic and test thoroughly.
- What is the role of the staking module?
It handles delegation, validator selection, bonding periods, and reward distribution.
Glossary of Key Terms
| Term | Definition |
| Tendermint BFT | A Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus engine used in Cosmos chains. |
| Unbonding Period | The time a delegator must wait to withdraw staked tokens. |
| Slashing | Penalty for validators who misbehave or go offline. |
| IBC | Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol for cross-chain data and token transfers. |
| CosmWasm | A module that enables smart contract functionality in Cosmos SDK-based chains. |
| Genesis File | Initial config file used to launch the blockchain. |
References
- Surmont, J., Wang, W., Van Cutsem, T. (2023). Static Application Security Testing of Consensus-Critical Code in the Cosmos Network. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.10613
- Oderbolz, N., Marosvölgyi, B., Hafner, M. (2024). Towards an Optimal Staking Design: Balancing Security, User Growth, and Token Appreciation. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.14617
- Cosmos SDK Documentation. https://docs.cosmos.network